What happens when your power system is overloaded or short-circuited? Even short interruptions can lead to operational disruptions, equipment damage and costly business delays. Electrical failure is one of the main causes of commercial building fires that account for 6.2 % of non-residential building fires.
Miniature circuit breakers ( MCBs ) can effectively prevent the above situation and provide accurate and reliable protection for your electrical infrastructure.
In this article, we will explain what miniature circuit breakers are, their working principles and their advantages.
What is a Miniature Circuit Breaker?

A miniature circuit breaker is an electrical switch that automatically shuts down the circuit when the network is in an abnormal state that includes overload and fault conditions.
Today, we use MCB instead of fuses in low-voltage power grids. The fuse may not be sensed, but miniature circuit breakers can detect more reliably. The MCB is much more sensitive to overcurrent than the fuse.
The MCB is electrically safer than a fuse. If a fuse occurs, the power supply can be quickly restored because the fuse must be rewired or replaced to restore the power supply. It can be easily restored just by turning on. Let ‘s look at the internal structure and working principle of miniature circuit breakers.
Read more : The difference between MCB and MCCB
What is Inside Miniature Circuit Breaker?
We need to view its internal structure to understand the superiority of MCB. If you look at the standard miniature circuit breaker drawing, you will usually find the following key components working together :
Main Contacts: These contacts carry load current and connect the inlet and outlet lines of the circuit.
Tripping Unit: This is the core component of the miniature circuit breaker, which monitors the current in the circuit and trips when there is an overcurrent or short circuit. The tripping unit is composed of bimetallic strip, magnetic actuator and actuator.
Terminals: These are the connections of the inlet and outlet lines.
Enclosure: Enclosure is used to protect the insulation between the miniature circuit breaker components and other electrical components.
Trip Indicator: miniature circuit breaker is usually equipped with a visual indicator to show whether the circuit breaker is in the ‘ on ‘ or ‘ off ‘ position.
Auxiliary Contacts: Some miniature circuit breakers have additional contacts that can be used to switch auxiliary loads or provide signal functions.
Operating Mechanism: It includes a handle and a lock, which is used for manual switching and automatic tripping.
Tripping Spring: This is the spring mechanism that fixes the MCB contact in the ‘ open ‘ position. When the tripping unit works, the tripping spring is released, so that the contact is separated and the circuit is disconnected.
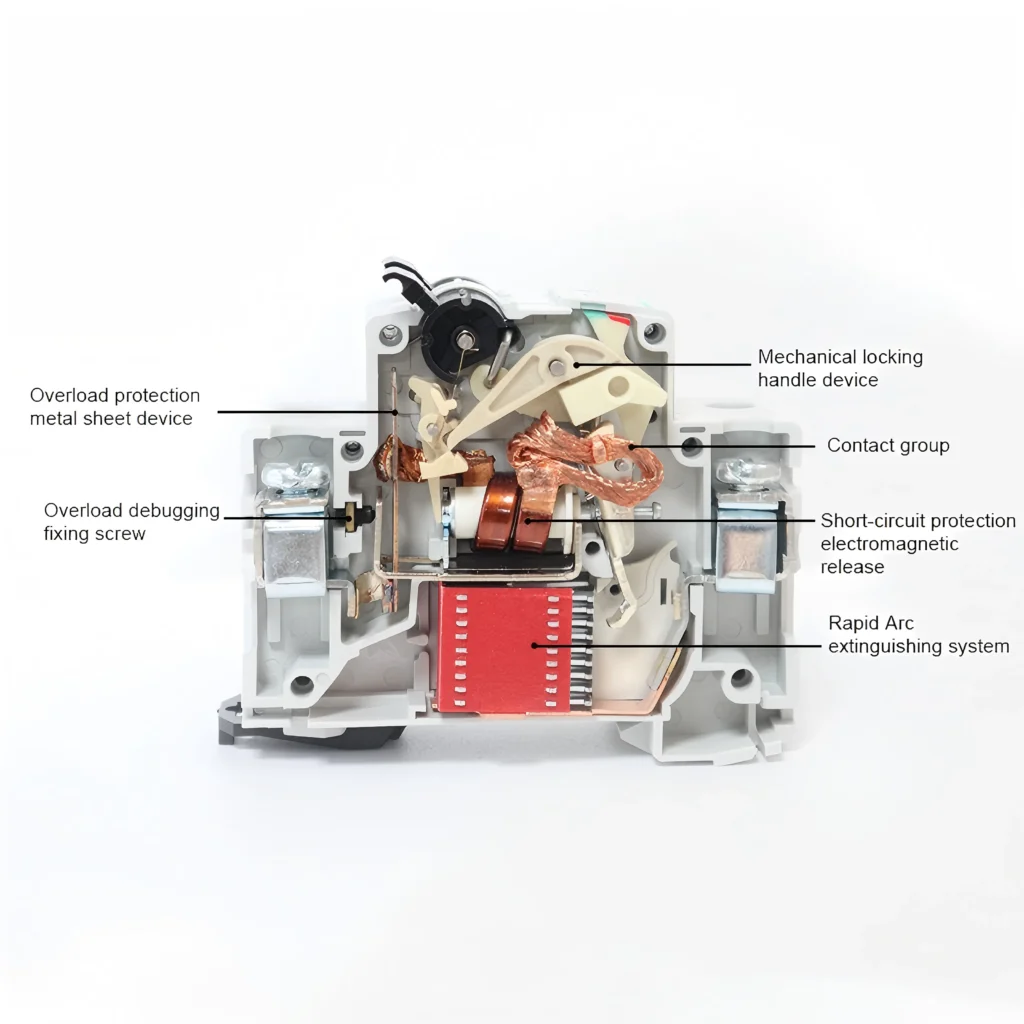
Miniature Circuit Breaker Working Principle
The miniature circuit breaker detects abnormal conditions in the circuit such as overload or short circuit and cuts off the current flow to prevent potential damage. Miniature circuit breaker provides a reliable and fast response solution for protecting electrical systems that reduce the risk of fire, equipment damage and expensive downtime.
Current Flow Monitoring: miniature circuit breaker continuously monitors the current in the circuit.
Fault Detection
Overload Protection: If the current exceeds the rated capacity ( overload ) for a long time, the MCB ‘s thermal mechanism ( bimetal strip ) will heat and bend. This action will trip and disconnect the circuit.
Short-circuit Protection: In the event of a short circuit ( sudden current surge ), the electromagnetic mechanism of the miniature circuit breaker will be activated immediately that will trigger the circuit breaker to trip within milliseconds and stop the current flow.
Tripping Mechanism
Thermal Mechanism: Suitable for progressive overload of current.
Magnetic Mechanism: rapid response to the rapid surge of current caused by a short circuit.
Circuit Disconnection: Once a fault is detected, the MCB trips that cause the circuit to be interrupted to prevent further damage to the wiring and connect equipment, or the overall electrical system.
Reset MCB: After the fault is cleared, the miniature circuit breaker can be reset manually to restore the circuit to normal operation.
Miniature Circuit Breaker Operation
One of the most common reasons for MCB tripping is that someone accidentally plugs two devices ( such as a microwave oven and a benchtop grill ) into the same circuit and opens them at the same time. We need to go to the distribution box to switch the switch back to the ‘ on ‘ position of the junction box, or replace the miniature circuit breaker with a deformed bimetallic light strip.
When the strip deforms, the spring attached to the latch moves to separate the contacts. When a short circuit occurs, the magnetic field in the coil will cause the plunger to move, so that the lock and the contact are separated. The force involved is called magnetomotive force (MMF).
You can move the lever outside the MCB to separate the contacts. If you choose to reset the miniature circuit breaker instead of replacing it, you can move the lever in the opposite direction after adding a new bimetal strip or a reset spring and plunger.
When the contact is separated, an arc may be generated. The structure of the circuit means that the arc will enter multiple shunts through the runway for safe quenching. Similarly, if the miniature circuit breaker is reset rather than replaced, after completing all the reset steps ( including replacing the fault line in the case of a short circuit ), the miniature circuit breaker is ready and the circuit can be reopened.
What is the Advantage of Miniature Circuit Breaker?
Resettable: it can be reset without replacement after tripping, which reduces the long-term maintenance cost.
Higher Sensitivity: Induction of current changes is more accurate than fuses and can better detect small overload currents.
Fault Isolation: When a fault occurs, the position of the switch handle can visually display the fault circuit, which is convenient for troubleshooting.
Safe Operation: The operator can restore power supply without contacting the live parts.
Miniature Circuit Breaker Types
The classification of MCB is diverse mainly based on poles and tripping current.
When purchasing, you also need to know miniature circuit breaker sizes.
Classified by Poles
| MCB Poles Classification Table | ||
|---|---|---|
| Type | Character | Application |
| Single Pole | Protect a fire line. | Single-phase home circuits, such as lighting |
| Double Pole | A double pole miniature circuit breaker can cut off the fire line and zero line at the same time. | Single-phase main switch, water heater, etc. |
| Triple Pole | 3 phase miniature circuit breaker to protect three fire wires. | Industrial motor, three-phase equipment |
| Four Pole | Protect three fire lines and one zero line. | Three-phase four-wire distribution system |
Classified by Tripping currents
Type A
Type A miniature circuit breaker is designed to trigger the circuit to trip when the current exceeds 2-3 times the rated current. It is particularly sensitive to short circuits that are suitable for semiconductor manufacturing.
Type B
Type B miniature circuit breaker is designed to quickly disconnect the circuit when the current exceeds three to five times the rated current. It is typically used for smaller loads with smaller switching surges such as residential or light commercial applications.
Type C
Type C miniature circuit breaker is designed to cut off the circuit immediately when the current exceeds five to ten times the rated capacity. Usually, this MCB is used for devices with high inductive loads, such as small motors and fluorescent lamps, which experience switching surges. It is usually more suitable for applications requiring higher short-circuit current such as commercial and industrial devices with high induction loads.
Type D
Type D miniature circuit breaker is designed to trip instantaneously when the current exceeds ten to twenty-five times the rated capacity. They are usually used for high-inductive loads, which are expected to frequently have high inrush current surges.
Type K
Type K miniature circuit breakers can tolerate 8 to 12 times the current of the rated capacity. It is commonly used in heavy-duty equipment such as compressors, hoist motors and X-ray machines.
| Comparison Table:The Mini & Max Tripping Current of Different MCB | ||
|---|---|---|
| MCB Type | Minimum trip current | Maximum trip current |
| Type A | 2lr | 3lr |
| Type B | 3lr | 5lr |
| Type C | 5lr | 10lr |
| Type D | 10lr | 20lr |
| Type K | 8lr | 12lr |
Applications
| MCB Application Summary Table | |
|---|---|
| Applications | Description |
| Residential electrical system | MCB protects home wiring and appliances from overload and short circuit to ensure home safety. |
| Industrial control panel | MCB protects industrial machinery and control panels from damage caused by electrical faults. |
| Commercial buildings | MCB is used to protect lighting systems, HVAC systems and power distribution circuits in commercial buildings. |
| Motor protection | MCB protects the motor from overload and short circuit to ensure its safe and efficient operation. |
| Automation system | MCB protects sensitive electronic equipment and reduces the risk of downtime due to electrical failures in automation systems. |
| Renewable energy systems | MCB is used in solar and wind energy devices to protect the circuit from failure and ensure stable operation. |
| Data center | MCB protects critical data center equipment from electrical problems and ensures continuous operation without interruption. |
| Marine and Aerospace Systems | MCB is used in ships and aircraft to protect the electrical system from damage caused by faults and ensure safety under extreme conditions. |
Upgrade your electrical safety with QJC ‘s MCB

As a professional electrical protection expert, QJC Electric are committed to providing high-quality miniature circuit breaker solutions. If you are ready to improve the protection and performance of the electrical system, please contact us immediately. Explore our full range of products to help you choose the MCB that suits your needs.
What is the difference between MCCB and MCB?
MCCB ( molded case circuit breaker ) and MCB ( miniature circuit breaker ) are both circuit protectors.
MCB is suitable for residential and small load: current 6-63A, short-circuit capacity 6-10kA, small size.
MCCB is used for industrial and large load: current 100-2500A, short-circuit capacity 10-100kA, large volume, adjustable.
What is the main purpose of the MCB?
The MCB main protection circuit from overload and short-circuit damage, through the thermal magnetic mechanism automatically disconnected to prevent fire and equipment burned. It can be reset, easy to maintain, commonly used in residential panels, limiting current protection wiring.
Which is better, MCB Or RCD?
There is no absolute advantage and disadvantage, the two complement each other. MCB is used for anti-overload / short circuit protection equipment ; RCD is used for anti-ground fault / electric shock, personal protection. Experts suggest that RCBO be used in combination. RCD is better when the risk of electric shock is high and MCB is more practical when the load is high.
Is an MCB the same as a fuse?
Similar but not the same. As mentioned above, both of them are overcurrent-proof, but the fuse needs to be replaced at one time. MCB can be reset and respond faster. Users regard MCB as an upgraded version of fuse, which is more reliable and convenient.
Why does RCD travel but not MCB?
RCD is sensitive to small leakage current ( < 30mA ), such as grounding fault tripping. MCB needs a large current ( such as hundreds of amperes overload / short circuit ) to trigger. For example, electrical leakage or wet environment causes RCD jump, while MCB does not reach the threshold. It is recommended to check the fault source.