When it comes to protecting solar systems, DC surge protectors immediately come to mind. However, there’s another type of surge protector available on the market: AC SPDs. They’re very similar. This article will explain the differences between DC and AC SPDs.
What is a DC SPD? And why is it crucial for solar systems?
The core components within a DC SPD have extremely high resistance at normal voltages. When faced with a transient high-voltage surge, a DC SPD automatically responds within nanoseconds, diverting the excessive surge to the ground instead of to our equipment. These surges can originate from direct lightning strikes or induced lightning strikes: A lightning strike near the equipment creates a strong electromagnetic induction effect on the ground or power lines. Switching high-power devices on the same power grid and electrostatic discharge can also cause voltage surges.
Difference Between DC SPDs and AC SPDs?
| Item | DC SPD | AC SPD |
| Current protection type | Direct current – current flows in one direction | Alternating Current – Current that changes direction periodically |
| Main applications | Solar photovoltaic systems (between panels and inverters), battery energy storage systems, and electric vehicle charging stations. | Home/building main distribution box, industrial power grid, commercial facilities (protection of air conditioners, refrigerators, etc.) |
| Technical difficulty and design | Further complicating matters: DC current flows continuously and is more difficult to cut off. | Relatively simple: AC current crosses zero several times per second. |
| Voltage level | For higher system voltages (e.g. 600V, 1000V, 1500V are common in solar systems) | For standard grid voltage (e.g. 230V single-phase for household use, 400V three-phase for industrial use) |
| Installation location | Installed at the DC input of the inverter (after the solar panel and before the inverter). | Installed in the main distribution box (after the grid access point) |
Using an AC surge protector to protect a DC circuit may not effectively interrupt the arc during a lightning strike and cause subsequent equipment failure.
How to Choose the Right DC SPD for You in Four Steps?
Conform Your System Voltage
Check the maximum system voltage for your solar panel string (e.g., DC 1000V or DC 1500V). The maximum continuous operating voltage (Uc) of the selected DC SPD must be higher than this value.
Choose the Right Protection Type
The following diagram shows how different types of SPDs work together, depending on their installation location:
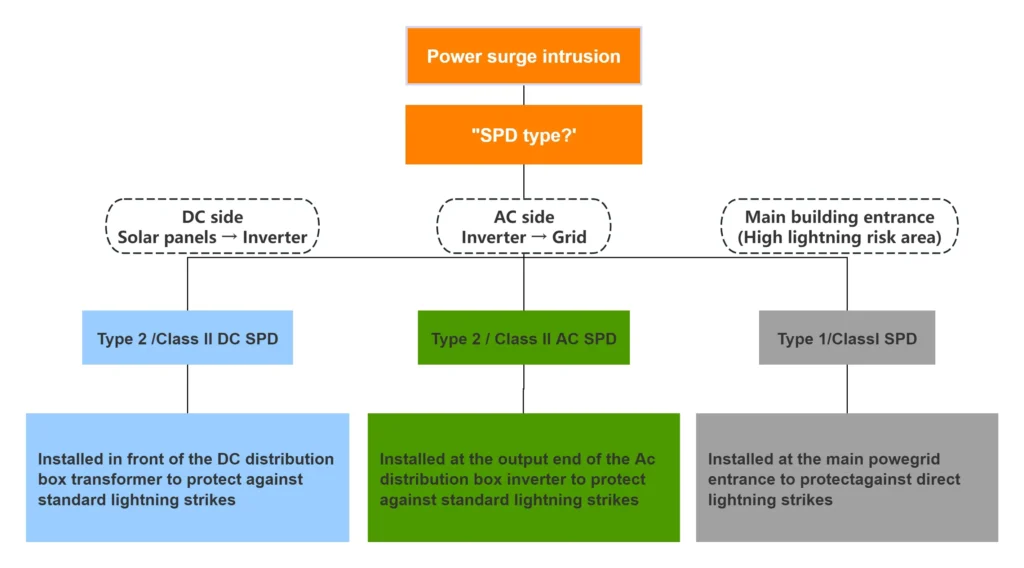
Focus on Key Protection Parameters
Voltage Protection Level (Up): the residual voltage ultimately applied to the device. The lower the Up value, the more comprehensive the inverter protection.
Nominal Discharge Current (In): Represents the SPD’s durability. A higher value generally indicates better resistance.
Check Safety Certifications
Be sure to choose products that comply with international or national technical standards such as IEC 61643-31 to ensure quality and safety.
What Benefits Does Installing a DC SPD Bring to Your Solar System?
Most importantly, a DC SPD protects the most expensive inverter. It prevents inverter burnout that avoids or reduces costly replacements. Secondly if surges cause system downtime, the interrupted power generation directly results in lost electricity revenue. Installing a DC SPD can reduce these unplanned downtimes and ensure continuous, stable power generation. Finally if without protection, surges can damage equipment and result in a risk of electric shock or even electrical fires that cause further property damage.
In the End
It is important for solar system owners to understand the differences between DC surge protective devices and AC surge protective devices. If mixed or interchanged, AC surge protective devices may adversely affect equipment. Equipping your equipment with the right DC surge protective device provides reliable safety and ensures stable and safe operation during wind, rain, and thunderstorms.