As electric vehicles (EVs) become increasingly popular, numerous inconveniences such as range anxiety have also happened. Many EV owners are searching for reliable and fast charging methods.
The new energy charging pile played a role as the primary EV charging equipment provides users with a convenient way to replenish energy and is an important infrastructure for electrified mobility.
What is a Charging Pile?
A charging pile is a device that transmits electricity from the grid to the car battery, providing power to electric vehicles. It can be found in various environments such as residential areas, commercial buildings and public places like parking lots or roadsides.
What types of charging systems?
1.Charging pile can be divided into AC charging pile and DC charging pile based on the output current.
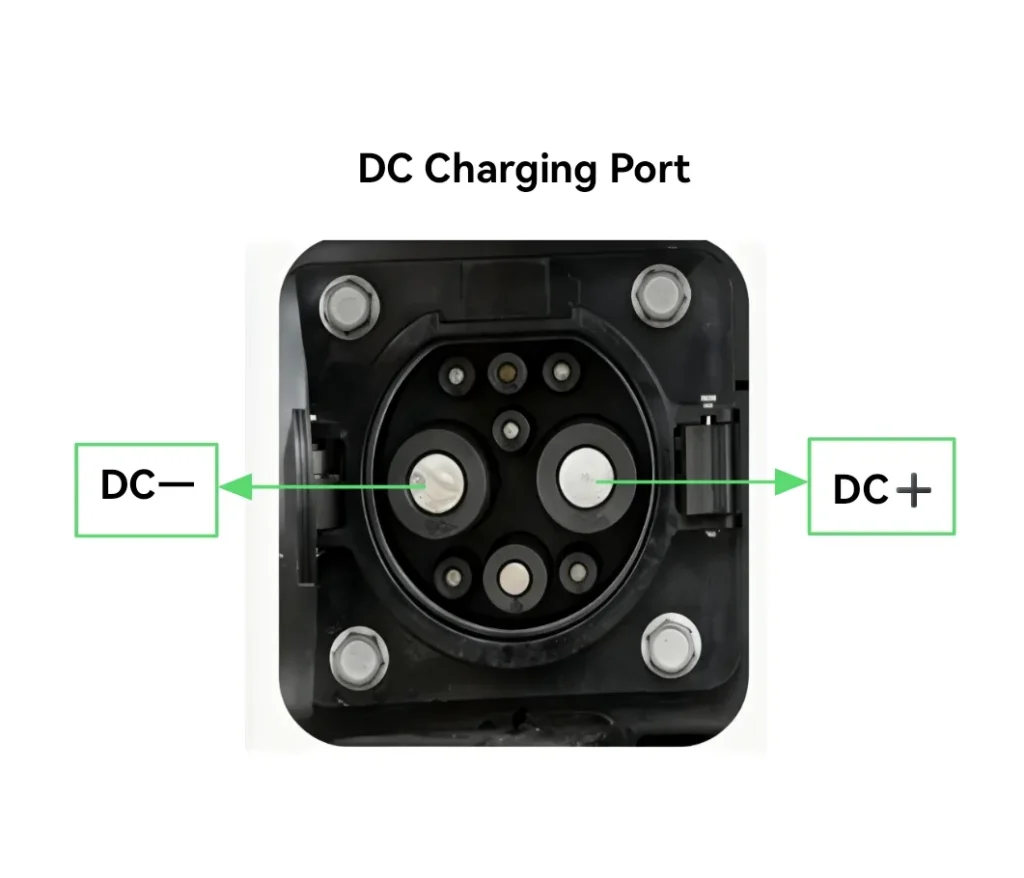
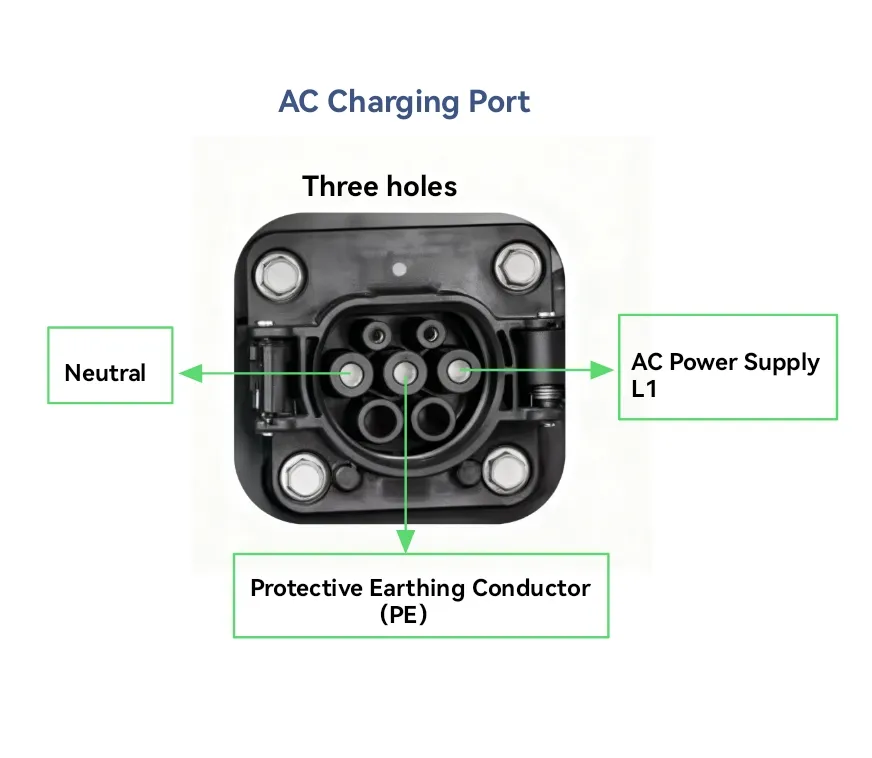

- AC charging pile: Output AC power;it requires the on-board charger to perform transformation and rectification. Limited by the on-board charger’s power, the power output is generally lower.
- DC charging pile: Input voltage uses three-phase four-wire (AC380V±15%, frequency 50Hz) and output adjustable DC power directly charges the electric vehicle’s battery.
Because DC charging piles use a three-phase four-wire power supply, they can provide power ranging from tens to hundreds of kilowatts that enable charging faster.
2.Charging pile can be divided into slow charging pile and fast charging pile based on charging speed.
- Slow charging pile: Those with a charging power of less than 22kW are slow charging piles that are suitable for applications in residential areas, workplaces and similar scenery.
- Fast charging pile: Charging power exceeding 22kW is classified as a fast charging pile that is suitable for use in charging piles, shopping mall parking lots, fleets and highways.
3.Charging piles can be divided into private piles and public piles based on usage scenery.
- Private pile: Installed in private parking spaces in residential areas that generally use AC slow charging.
- Public pile: Provide public charging services for vehicles that offer both DC and AC charging options.
| Charging pile types | Rated power | Application |
| AC slow charging station | 7kW,11kW,22kW | Residential communities, workplaces, charging pile |
| AC fast charging station | 40kW | Charging pile, shopping mall parking lots |
| DC fast charging station | 50kW-480kW | Charging pile, shopping mall parking lots, fleets, highways |
What are the benefits of an electric vehicle charging pile?
1. For car owners: Improved convenience, economy and experience (Freedom and convenience of energy replenishment)
Eliminate range anxiety
A widespread charging network across cities and highways allows car owners to travel with the same peace of mind as owners of gasoline-powered vehicles without excessive worry about their vehicles breaking down. Home charging stations especially offer the convenience : charge as soon as you get home, fully charged by dawn.
- Home slow charging: Meets daily commutes and regular lifestyles at the lowest cost.
- Public fast charging: Meets the needs of long-distance travel and emergency charging to save time.
- Destination charging: Charge conveniently while parking in shopping malls or office areas without taking up extra time.
Significantly reduced operating costs
- Far lower than fuel costs: The cost of electricity is far lower than that of gasoline. Especially when charging during off-peak electricity prices at home, the energy cost per kilometer may be only 1/5 or even 1/10 of that of a gasoline car.
- Low maintenance costs: The charging process itself has a simple mechanical structure, unlike internal combustion engines which have many parts requiring maintenance to further reduce long-term maintenance costs.
Enhance User Experience and Control
Flexible Charging Strategies: Owners can flexibly schedule charging times and methods based on their travel plans and electricity price fluctuations (peak and off-peak pricing) to optimize costs.
Remote Management and Reservation: A mobile app allows for remote control of home charging stations and monitors charging status. Reservation of available charging spots at public charging stations provides a highly intelligent and convenient experience.
2. For the Vehicle Itself: Optimizing Performance and Extending Lifespan
Ensure Battery Health (Especially for Slow Charging)
Shallow Charging and Discharging: Facilitates adherence to the “20%-80%” golden rule for battery maintenance. Regular slow charging causes less wear and tear on the battery compared to frequent DC fast charging that can maintain battery capacity and state of health (SOH) over the long term.
Battery Preheating Function: Many electric vehicles can preheat the battery while charging via an app or timer function in cold weather that ensure optimal performance and range during travel.
Ensure the Vehicle is Always in Optimal Condition
The convenient charging keeps the vehicle at a high battery level that meets the owner’s travel needs at any time.It also ensures the air conditioning, power and other systems do not operate normally due to insufficient battery power.
The Difference Between Charging Piles and Charging Stations

What is a Charging Station?
A charging station is a regional facility that centrally installs multiple charging piles that provides simultaneous charging services for multiple vehicles. It is often built in high-traffic areas such as highway service areas and commercial parking lots.
Key Features of Charging Piles
Basic Unit: It is the smallest functional unit that constitutes a charging network and can be installed and operated independently.
Flexible installation locations: It can be installed in any parking space with electricity supply such as private parking spaces, residential areas, shopping mall parking lots and roadsides.
Diverse Types: Mainly divided into AC slow charging piles (low power and slow charging) and DC fast charging piles (high power and fast charging) to meet different needs.
Relatively Single Function: The core function is to charge electric vehicles; it usually does not provide additional ancillary services.
Wide Range of Investment and Operating Costs: A simple AC charging pile has a lower cost, while a high-power DC charging pile costs significantly more. It can be invested in and managed by individuals, properties, or operators.
Key Features of Charging Stations
Integrated System: It’s not a single device, but a complete system comprising multiple charging piles, transformers, power distribution systems, monitoring systems and safety facilities.
Fixed Location & Large Scale:It requires dedicated space (multiple or even dozens of parking spaces) and involves specialized power capacity expansion and facility layout. Installation cannot be as flexible as with a single charging pile.
Comprehensive Functionality and Service
- Core function: Provides fast charging service for multiple vehicles simultaneously.
- Supporting Services: Typically equipped with rest areas, restrooms, retail stores and catering facilities to enhance the user experience while waiting.
- High Investment and Professional Operation
Construction and operation costs are very high due to the involvement of land, power capacity expansion, multiple sets of equipment, and supporting facilities. They are usually operated, maintained and managed by specialized companies.
What is the “80% Rule” for Electric Vehicles?
We mentioned the “20-80” rule above, but what exactly is it? The “80% rule” for electric vehicles is not a mandatory regulation, but a best practice recommendation to protect battery health, improve charging efficiency and ensure safety. Most electric vehicles automatically reduce their charging speed after the battery level reaches approximately 80%.
Why do I only need to charge my electric car to 80%?
Slowing down battery aging
Lithium-ion batteries (like mobile phone batteries) experience the greatest internal chemical stress when at extremely high or low charge levels. Maintaining a 100% charge for extended periods accelerates irreversible chemical reactions within the battery that lead to capacity decay and increased internal resistance.Finally the battery’s overall lifespan and driving range will shorten.
Providing space for regenerative braking
For electric vehicles, the vehicle converts kinetic energy into electrical energy to charge the battery through “regenerative braking” when you coast or brake. If the battery is fully charged (100%), energy recovery is not possible: this results in energy waste and affects braking performance.
Most importantly, 80% battery capacity is sufficient for daily commuting needs.
Learn more
By understanding charging piles and charging habits, electric vehicle owners can plan their charging more efficiently that make travel more convenient and worry-free. Stakeholders also can better support the adoption of electric vehicles and address shared challenges.
Whether you are a manufacturer, dealer or retailer, integrating charging stations into your business strategy is a forward-looking step towards a greener future.
