A distribution box (DB box) plays a vital role in electrical wiring systems, acting as a central hub where cables branch out to various outlets and switches within a building. It supports different cable sizes and types, enabling efficient and organized power distribution.
Crucial for both safety and functionality, the DB box ensures electricity is directed appropriately across the premises, providing convenient access and control over electrical circuits.
What is the difference between a consumer unit and distribution board?
The distinction between a consumer unit and a distribution board lies in their usage and capacity. Consumer units are typically found in residential properties, while distribution boards are more common in commercial or industrial settings.
A consumer unit offers a simple and adaptable way to distribute electricity from a single source to various outlets. It includes multiple switches designed to protect against short circuits and provides safe wiring options for homes.
In contrast, a distribution board is suited for larger installations requiring higher power capacity and thicker cables. It connects to multiple circuits, making it ideal for handling heavier electrical loads and more intricate wiring systems.
What is the meaning of a 4 way distribution board?
A 4 way distribution board is designed to handle up to four separate circuits, with each circuit capable of powering one or more outlets within a building. It ensures electricity is safely distributed from the main supply to these circuits, enabling efficient power management.
In comparison, 6 way and 12 way distribution boards can support six and twelve circuits, respectively. These larger boards offer greater capacity and flexibility for managing more devices and electrical connections within a system.
Regardless of size, all distribution boards play a critical role in electrical systems. They house cables, centralize circuit breakers, and ensure safe and efficient power restoration. Additionally, they simplify installation and maintenance by consolidating key components of the power distribution system into one accessible location.
How do I choose an electrical distribution board for home?
When selecting an electrical distribution board for a home, particularly for an HDB flat, it is essential to ensure the board complies with safety standards and can handle the electrical load efficiently. A key feature to prioritize is a mechanism that allows quick power disconnection, such as a main switch or circuit breakers, to prevent hazards caused by electrical faults.
The distribution board should be capable of safely routing electricity across various circuits, offering flexibility to meet different power requirements. Additionally, the board’s price should reflect its quality and capacity, ensuring it can accommodate future increases in power demand without compromising safety.
Proper selection not only ensures smooth power distribution but also simplifies maintenance and enhances the overall safety of the household electrical system.
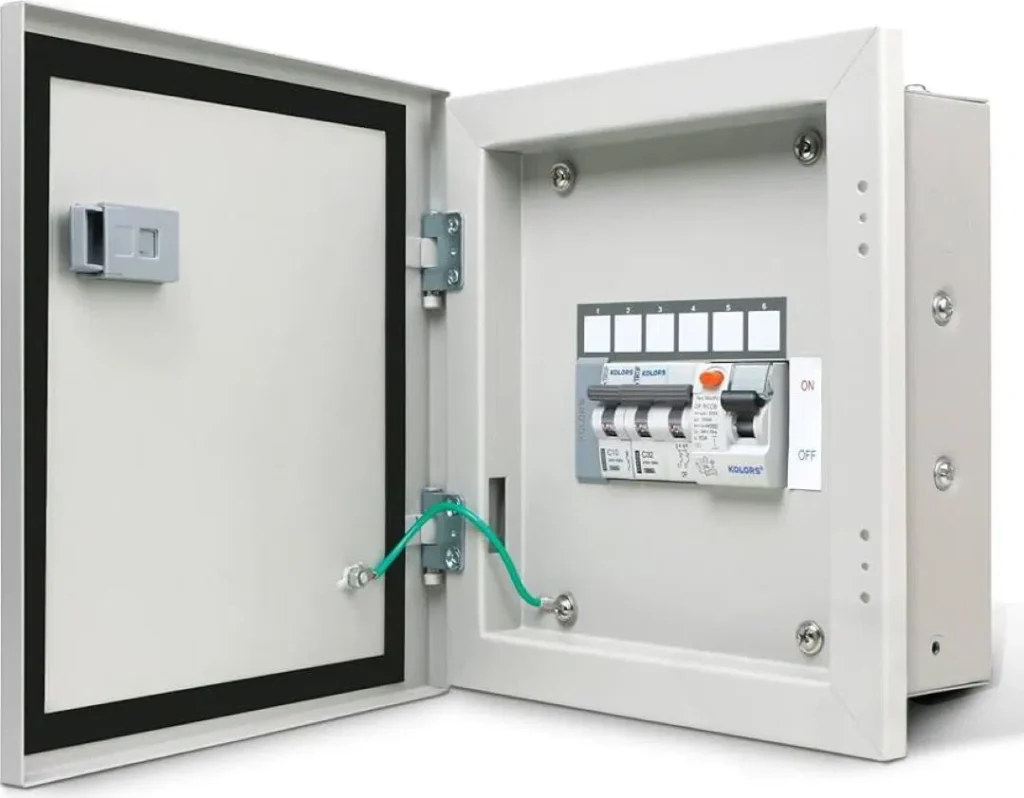

What is the purpose of a distribution box? – Power Distribution & Electrical Supply
A distribution box is essential for the safe and efficient distribution of electricity within an electrical system. It serves as a central hub where the electrical supply is balanced and routed across circuits, using components like circuit breakers and bus bars to prevent overloads, faults, or damage.
The primary function of a power distribution box is to evenly distribute the electrical load across circuits. This helps protect appliances and reduces the risk of electrical fires. Additionally, it provides a practical solution for managing power needs, offering easy access for maintenance and ensuring the electrical supply aligns with current usage demands.
By organizing components to safeguard and distribute electricity effectively, distribution boxes are crucial for maintaining a reliable and secure electrical system.
What is the purpose of a distribution board?
A distribution board is designed to divide an incoming electrical power supply into multiple subsidiary circuits, ensuring electricity is efficiently routed to different parts of a building or facility. It plays a vital role in maintaining safety by quickly tripping in case of faults, preventing potential hazards.
This component is essential for protecting both the circuits and connected devices within the electrical system. It is particularly useful in larger setups that require various electrical components and circuit breakers to guard against issues like short circuits or overloads.
By managing the flow of electricity, a distribution board ensures safe and controlled power distribution across all circuits. Its proper installation and use are crucial for maintaining a secure and reliable electrical system.
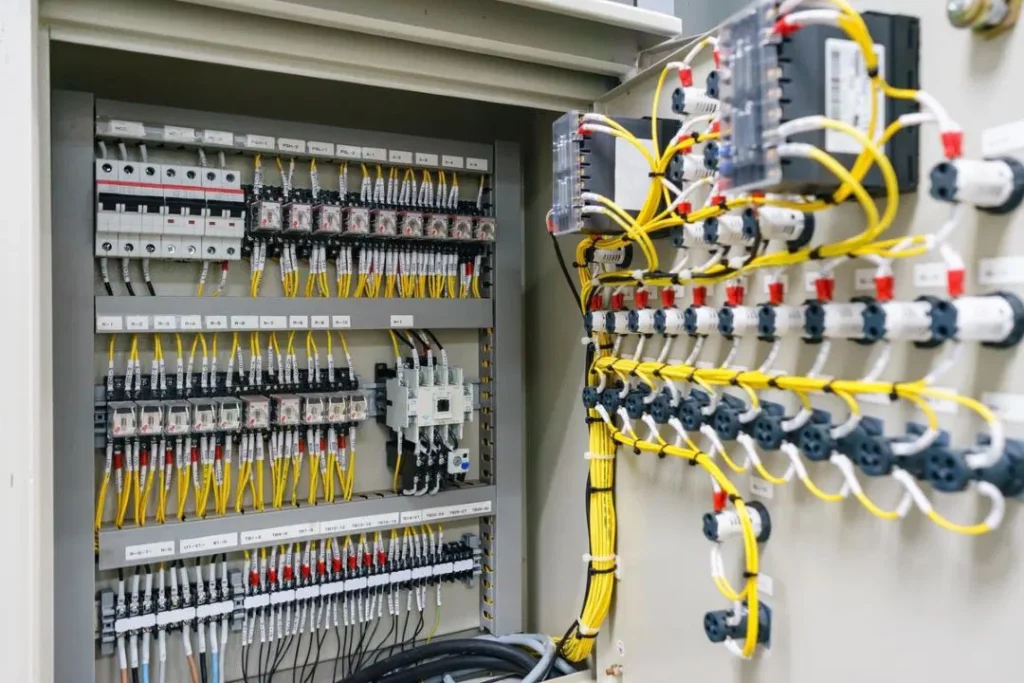
What is a power distribution box used for?
A power distribution box is designed to safely channel electricity from the main power source to multiple devices or circuits. It acts as a central hub, ensuring efficient and organized power distribution throughout an electrical system.
This device plays a critical role in managing the flow of electricity while protecting the system from potential hazards like overloads or faults. Equipped with components such as circuit breakers and fuses, it safeguards both the circuits and connected devices, maintaining a safe operational environment.
By centralizing control, the power distribution box enhances safety and optimizes the efficiency of electrical supply across various circuits. This setup simplifies management, ensuring reliable and secure power distribution for residential, commercial, or industrial needs.
What does the distribution panel do?
A distribution panel divides an incoming electrical power supply into multiple subsidiary circuits, ensuring electricity is distributed effectively throughout a facility. It plays a key role in directing power to various outlets, optimizing the performance of each circuit.
By managing the flow of electricity, the panel ensures safe and efficient power delivery to different areas of a building. This helps prevent overloads while providing each outlet with the required current to operate correctly.
