PV cables play a vital role in ensuring solar installations are both reliable and meet code requirements. Designed specifically to adhere to industry standards, they safeguard your investment and help your solar energy system operate efficiently. This overview explains the importance of PV cables and their significant contribution to the success of your project.
What is a PV Cable?
A photovoltaic (PV) cable, also known as a solar cable, is a unique electrical cable created specifically for photovoltaic systems. These systems generate electricity from sunlight through solar panels. PV cables link solar panels to various system components, including inverters, charge controllers, and battery storage units.
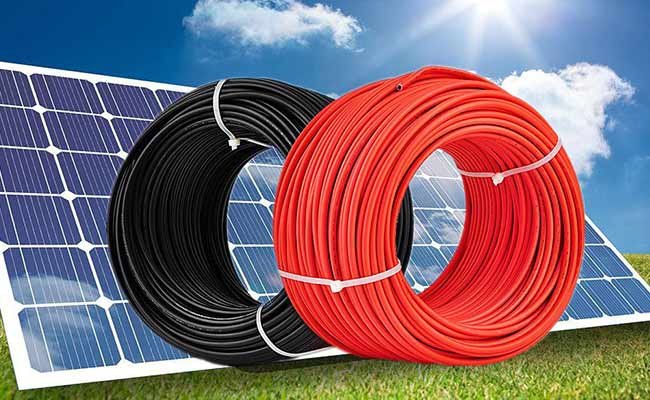

Differences Between PV Cables and Normal Cables
PV cables offer several distinct advantages over regular electrical cables:
- UV Resistance: Designed for outdoor use, PV cables can endure extended sunlight exposure without deteriorating.
- Weatherproofing: Built to resist harsh conditions, they can withstand moisture, rain, and extreme temperatures.
- Flexibility: Their flexible construction allows for easier installation, especially around corners or obstacles in solar systems.
- High-Temperature Tolerance: PV cables are capable of handling the high temperatures caused by sunlight and electrical currents.
- Insulation: These cables feature robust insulation, typically made from materials like cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) or ethylene propylene rubber (EPR), ensuring protection against electrical shocks, short circuits, and environmental damage.
- Low Smoke Zero Halogen (LSZH): Many PV cables are made with LSZH materials to minimize toxic gas and smoke emissions during a fire, enhancing safety for indoor setups or densely populated areas.
PV cables are also color-coded for easy identification (red for positive (+), black for negative (-)). These features are crucial for ensuring the safety and efficiency of solar power systems.
Components of PV Cables
PV cables are designed with components that ensure durability, flexibility, and resistance to environmental challenges. These key components include:
- Conductor: The conductor carries the electrical current and is typically made of copper due to its excellent conductivity, flexibility, and durability. Aluminum is sometimes used as a more affordable alternative.
- Insulation: Surrounding the conductor, the insulation prevents electrical shocks and short circuits. Common materials for PV cable insulation include cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE), ethylene propylene rubber (EPR), or thermoplastic elastomers (TPE). These materials provide strong electrical insulation and resist heat, UV rays, and harsh weather.
- Jacket/Sheath: The outer jacket protects the cable from mechanical damage, abrasion, moisture, UV radiation, and other environmental factors. It is often made from durable polymers like polyvinyl chloride (PVC), XLPE, or halogen-free flame-resistant materials.
- Filler Material: Some cables include filler materials such as non-conductive powders or fibers to improve flexibility, reduce stress on the conductor, and enhance mechanical strength.
- Tape/Wrapping: Additional layers of tape or wrapping may be applied to provide extra protection against moisture, abrasion, or mechanical damage.
The choice of materials depends on factors such as the application, environmental conditions, regulations, and industry standards. Selecting cables with components suited for outdoor use is essential for the reliability of solar energy systems.
Applications of PV Cables
PV cables are critical components in the solar energy sector, specifically designed for photovoltaic systems that convert sunlight into electricity. Below are their primary applications:
- Solar Power Plants: In large-scale solar facilities, often called solar farms or parks, PV cables are used to connect components and transmit electricity generated by solar panels.
- Residential Solar Installations: These cables link solar panels to inverters and other system parts in home-based solar setups, enabling clean energy generation for household use.
- Commercial and Industrial Solar Installations: PV cables are essential in larger systems for businesses, factories, and institutions, ensuring efficient electricity transmission between solar panels and the required components.
- Off-Grid and Remote Solar Systems: In areas without access to the main power grid, PV cables help connect solar panels to batteries and other equipment, providing self-sufficient energy solutions.
- Solar Street Lighting: These cables power standalone solar lighting systems for streets, parks, and public spaces by connecting solar panels to batteries and lights.
- Solar Water Pumping: PV cables are used in systems that pump water using solar energy, offering reliable solutions for irrigation and water supply, especially in remote areas.
These applications highlight the versatility of PV cables in supporting various solar energy projects across residential, commercial, industrial, and off-grid sectors.
Disadvantages of PV Cables
PV cables, while essential for solar energy systems, come with several drawbacks:
- Cost: Due to their specialized design, materials, and manufacturing processes, PV cables are more expensive than standard electrical cables. However, their durability and reliability often justify the higher initial investment.
- Size and Weight: These cables are generally bulkier and heavier compared to regular electrical cables, which can make handling and installation more challenging.
- Installation Challenges: PV cables require specific connectors and installation techniques tailored for solar applications, which may complicate the setup process.
- Limited Recyclability: The unique materials used in PV cables make them harder to recycle at the end of their lifespan compared to standard copper wiring.
Despite these disadvantages, PV cables remain a critical component for ensuring the efficiency and longevity of solar energy systems.
How to Choose the Right PV Cable
Selecting the right PV cable is crucial for ensuring the efficiency, safety, and durability of your solar energy system. Here are the key factors to consider:
- Compliance with Standards: Ensure the cable meets industry certifications and standards, such as IEC or UL, to guarantee safety and reliability.
- Material Quality: Opt for cables made from high-grade materials suitable for outdoor use. Copper conductors are preferred for their excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. Insulation and sheathing materials like XLPE, PVC, or LSZH provide durability and protection against UV radiation, heat, and weathering.
- Proper Sizing: Choose a cable size that matches the system’s current rating, voltage drop, and the distance between components to ensure optimal performance.
- Voltage and Current Ratings: Select cables with ratings that align with your system’s requirements to prevent overloading or inefficiencies.
- Temperature Rating: Verify that the cable can operate safely within the temperature range of your installation environment without degrading.
- Flexibility and Bend Radius: Look for flexible cables with a small bend radius to simplify installation and routing around obstacles.
- Warranty and Manufacturer Reputation: Choose cables from reputable manufacturers offering strong warranties to ensure long-term reliability.
- Affordability: Evaluate the initial cost alongside factors like installation ease, maintenance needs, and lifespan to determine long-term value.
Tips for Using PV Cables Effectively
To ensure the safety, efficiency, and longevity of your PV cables, follow these practical tips:
- Install Correctly: Follow industry standards, manufacturer instructions, and local electrical codes during installation.
- Avoid Overloading: Ensure the cable’s current capacity is not exceeded to prevent overheating or damage.
- Consider Temperature Range: Use cables rated for the environmental temperature conditions to avoid performance issues or degradation.
- Protect from Damage: Safeguard cables from physical harm, moisture, and harsh environmental factors by using proper protective measures.
- Terminate and Connect Properly: Use suitable connectors, terminals, or junction boxes to securely connect cables to solar panels, inverters, and other components.
- Inspect Regularly: Check cables and connections periodically for wear, damage, or signs of deterioration.
- Maintain Proper Documentation: Keep detailed records of your cable installation to make troubleshooting easier in the future.
By adhering to these guidelines, you can enhance the reliability and performance of your PV cables and solar energy systems over time.
