Electrical Symbols play a crucial role in understanding and designing electrical circuits.
From fuses to circuit breakers, each symbol represents a specific component and its function.
This guide simplifies these symbols, helping you decode their meanings and applications in electrical systems.

The image illustrates various symbolic representations of a fuse commonly used in electrical circuits. A fuse, designed to safeguard electrical devices from overcurrent, contains a thin wire or metal strip that melts under excessive current, thereby interrupting the circuit and halting the flow of faulty currents. Standards such as IEC, IEEE, and ANSI define these symbols, which vary in appearance but serve the same protective purpose.

The image depicts the symbol for a Fuse Switch, which combines the functionality of a fuse and a switch in electrical circuits. A Fuse Switch operates by physically removing the fuse, as the fuse itself is an integral part of the switch mechanism. This design ensures both circuit protection and manual control over the electrical connection.

The symbol shown represents a thermal fuse, a temperature-sensitive safety device used in electrical circuits. Unlike standard fuses, a thermal fuse operates based on temperature rather than current, unless the current generates enough heat to exceed the threshold temperature.
When the ambient temperature surpasses its rated limit, the internal fusible element melts, breaking the circuit and preventing overheating or potential fire hazards.
Thermal fuses are commonly used in appliances like hair dryers, coffee makers, and motors to ensure safety by cutting off power during abnormal temperature rises.

The provided symbol represents a fuse switch disconnector, which combines a fuse and a switch in series. This device serves dual purposes: it allows manual switching of the circuit and provides overcurrent protection by breaking the circuit when the current exceeds safe limits. It is widely used in electrical systems to ensure both operational safety and ease of maintenance.

This is the symbol for an Isolator Switch Disconnector, used to isolate and fully de-energize a circuit for safety during maintenance.

This is the symbol for a Fast Blow Fuse, which instantly blows when the current exceeds its rated limit. It is commonly used to protect sensitive electrical equipment from overcurrent.

This is the symbol for a Slow Blow Fuse, which can tolerate high current surges for a short time before blowing. It is ideal for devices like motors that require high starting currents.

This is the symbol for a Fuse with Striker, which includes a striker pin that acts as an indicator. The pin pops out when the fuse blows, showing its condition.

This is the symbol for a Fuse With Alarm Contact, which includes a built-in alarm circuit. When the fuse blows, the alarm activates, providing a visual or audible indication of the fault.

This symbol represents a fuse with separate alarm contact.

This is the symbol for 3 Linked Fuses with Release of Any Striker, where all three fuses are interconnected and release together if any one of the strikers is triggered.

This is the symbol for an Oil Type Fuse, used in distribution switchgear immersed in oil. The oil acts as a coolant, enhancing the fuse’s breaking capacity.

These are symbols for a Circuit Breaker, an automatic switch that protects electrical systems from short circuits or overloads. It opens the circuit when the current exceeds its maximum limit.

This is the symbol for a Non Draw-out Circuit Breaker, which is fixed-mounted and requires power flow to be stopped during maintenance.

This is the symbol for a Draw out Circuit Breaker, consisting of a fixed base and a removable sliding breaker. It allows maintenance without interrupting the power flow, making it ideal for systems requiring continuous power.

The symbol represents a Thermal Switch, which operates based on temperature changes. It opens the circuit when the temperature exceeds its set limit and closes it when the temperature drops below a certain point.

This is the symbol for a Network Protector, used between the secondary terminal of a distribution transformer and the load network. It disconnects the transformer when reverse current flow is detected, preventing energy loss and ensuring system stability.

This symbol represents a threaded circuit breaker.

This is the symbol for a Single Pole Circuit Breaker, which has one hot wire. It trips to disconnect the circuit in case of overload or short circuit.

This is the symbol for a Double Pole Circuit Breaker, which has two hot wires. It trips both lines simultaneously in case of an overload or short circuit, ensuring safety in 240-volt circuits.

This is the symbol for a Three Poles Circuit Breaker, used in three-phase systems. It connects all three phases and trips simultaneously in case of overload or short circuit in any phase, ensuring system protection.
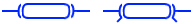
This is the symbol for an Isolator Circuit Breaker, a manual off-load device used to completely disconnect the load from the source. It has a lower current capacity than standard circuit breakers and provides visual confirmation of an open circuit, ensuring safety during maintenance.

This is the symbol for a Lightning Arrester / Surge Protector, a device used to protect electrical systems from lightning or high surge currents. It diverts excess current to the ground through its high-voltage and ground terminals.

The image shows symbols for a Spark Gap, a device consisting of two conductors separated by a gas-filled gap. When the voltage exceeds the gas’s breakdown point, the gas ionizes, creating a spark. Spark gaps are used in spark plugs for fuel ignition and in pulse power applications like capacitor discharge at high voltage or current.

This is the symbol for a Double Spark Gap, which features two small gaps between conductors to create double sparks. It is commonly used in high-voltage applications and spark plugs.

This is the symbol for a Surge Arrestor / Gas Discharge Tube, a device with a hermetically sealed gas chamber. When the voltage exceeds a certain limit, an arc forms, creating a short circuit to divert the surge current and protect connected equipment.

This is the symbol for a Telephone Line Protector, designed to safeguard telephone lines from surges or lightning strikes. It prevents damage to conductors and connected equipment by diverting excess voltage safely to the ground.

This is the symbol for a Lightning Rod, a metal rod installed on buildings to protect them from lightning strikes. It directs the lightning’s energy safely to the ground, bypassing the structure and preventing damage.

This is the symbol for a Thermostat, a device that regulates temperature by switching heating or cooling equipment on and off. It maintains the desired temperature by responding to changes in the surrounding environment.

This is the symbol for a Cartridge Circuit Breaker, which holds a cartridge fuse. The fuse breaks when the current exceeds its limit and can be easily replaced.
