Some people might say a DB box is just a box. But when someone says “I’m going to check out the distribution box” , they’re likely referring to the entire box on the wall with a lid that includes the distribution board inside. In this situation the distribution box obviously means the entire device. Today electrical systems are crucial for homes and industries. But what exactly is a distribution box and why is it so important in our daily lives?
What is a Distribution Box (DB Box)?
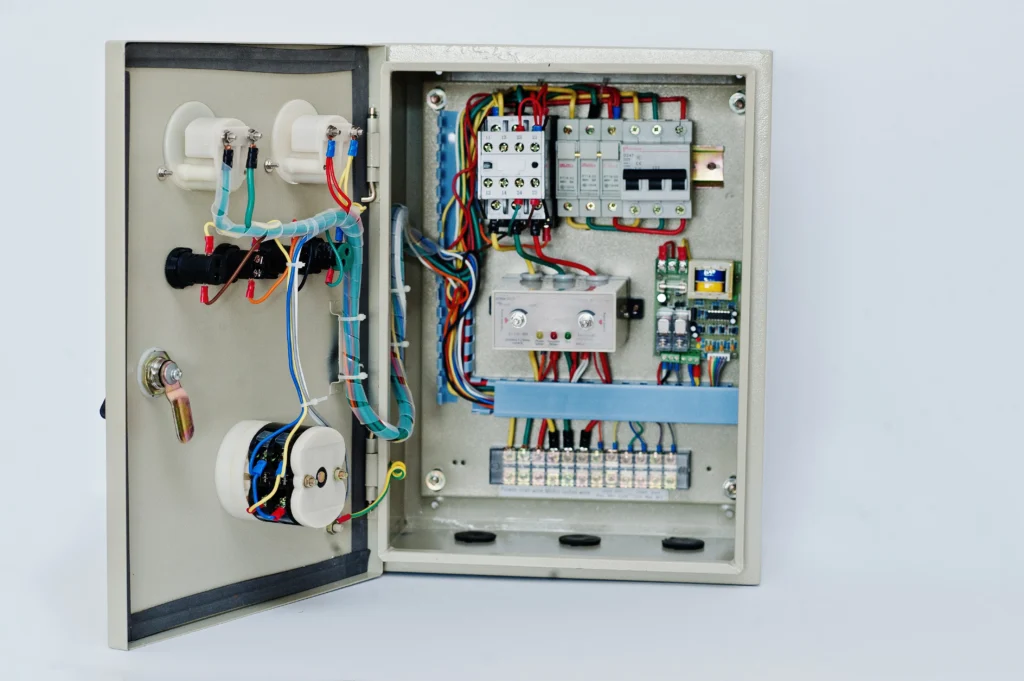

A distribution box (DB box) is an essential piece of equipment in an electrical system. It distributes power from a single input source to various circuits throughout a building using internal electrical components such as circuit breakers, fuses and terminals. Whether in a home, office or factory, a DB box ensures safe and efficient use of electricity. It distributes power to different devices and systems.
The primary function of a distribution box is to provide a safe and organized way to manage circuits. It acts as a protective enclosure, housing multiple critical components such as circuit breakers, fuses and busbars. These components work together to prevent electrical faults (such as short circuits or overloads) from damaging the electrical system.
Main Components of a Distribution Box
Outer Shell
· The outer shell is the physical structure of the distribution box that primarily provides protective, support and isolation functions.
· Box Body: Primarily made of metal and insulating materials that contains an internal mounting plate for securing internal electrical components and has cable entry/exit holes on all four sides.
· Box Cover/Door: An openable panel used to conceal and operate internal components that usually has a transparent observation window for viewing the internal switch status without opening the door. The inside of the door typically has circuit labels to identify the circuit corresponding to each switch.
· Mounting Lugs/Brackets: Structures on the sides or back of the box for mounting that facilitate embedding or surface mounting of the distribution box to walls or brackets.
· Knockout Holes: Small pre-drilled holes around the box that can be easily knocked out when needed, used for the entry and exit of cables and conduits; their positions are flexible and adjustable.
Internal Electrical Components
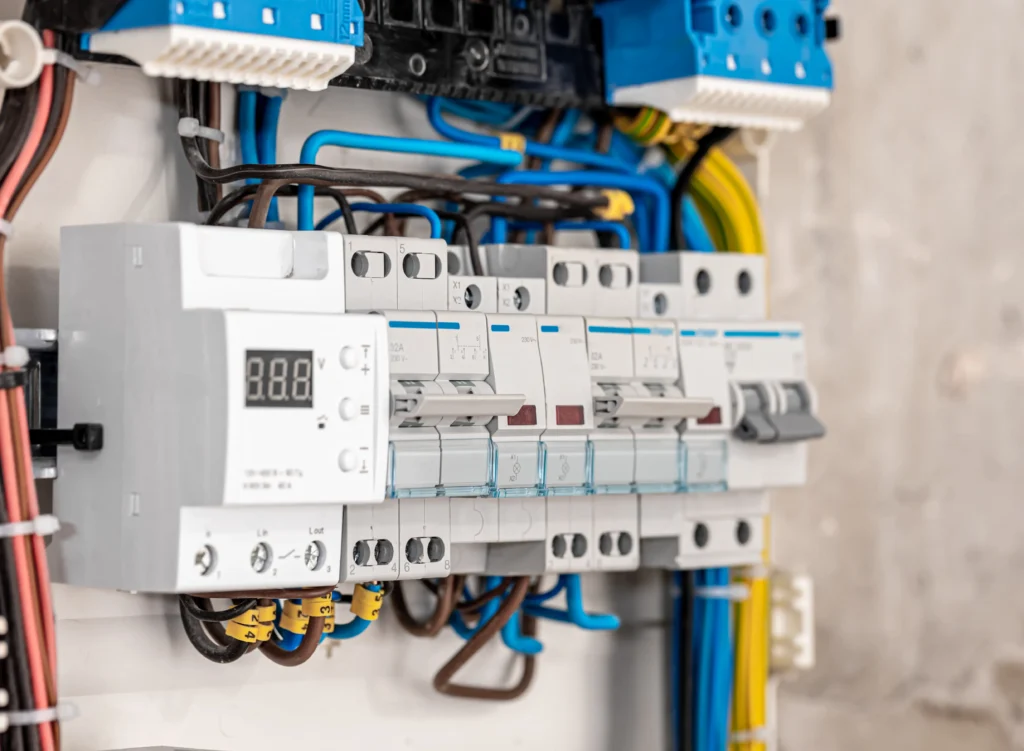
· Main Circuit Breaker: This is the main switch for the entire user-side circuit. When a comprehensive electrical maintenance is required, pulling this switch will disconnect the power supply to all circuits within the distribution box (except the incoming line). It is usually the largest capacity 2P (single-phase) or 3P (three-phase) circuit breaker that is located at the very beginning of the distribution box.
· Branch Circuit Breakers: Each independent circuit is equipped with a branch circuit breaker responsible for overload and short-circuit protection for that line. Miniature circuit breakers are most commonly used that offer only basic overload and short-circuit protection.
· Residual Current Device (RCD): Detects leakage current. When current leaks to ground due to insulation damage in a circuit or equipment and the leakage current reaches a dangerous level (typically 30mA), it will automatically cut off the power supply within a very short time (<0.1 seconds), effectively preventing electric shock and electrical fires.
· Surge Protector: Typically installed after the main switch, it prevents damage to expensive household appliances (such as televisions, computers, and refrigerators) caused by instantaneous overvoltage (surges) due to lightning strikes or internal power grid switching operations. It conducts instantaneous high-voltage surges to the ground.
Conductors and Connection Systems
· DIN Rail: All modular circuit breakers and residual current devices (RCDs), etc., can be easily and neatly installed on this rail using the clips on their backs.
· Busbars:
Neutral Busbar: A copper busbar that collects the neutral wires of all branch circuits. All branch circuit neutral wires are connected here.
Ground Busbar: A copper busbar that collects the ground wires of all branch circuits. All circuit ground wires (yellow-green) and equipment ground wires are connected here that ultimately connect to the earth.
· Internal Wiring: Insulated wires used to connect the main switch, branch switches and busbars.
Types of DB Box
By Voltage Level
· Low-Voltage Distribution Box: Voltage level is AC 1000V and below.
· High-voltage distribution boxes/cabinets: Voltage level is AC 10kV and above.
By Application and Function
· Main distribution box: is responsible for receiving electrical energy from transformers or the municipal power grid; provide overall control, protection metering of the electrical energy for the entire building or area. Located at the entrance of the power supply system such as the main distribution room of a building. It has a large capacity and high protection level that usually include a main circuit breaker, metering instruments, etc.
· Sub-distribution Box: Redistributes the electrical energy from the main distribution box to smaller areas or terminal distribution boxes that are located downstream of the main distribution box and in various floors or functional areas. It has a medium capacity with circuit breakers configured according to the area load.
· Terminal Distribution Box: Directly provides power, control and protection (such as short-circuit and overload protection) for terminal electrical equipment. Located closest to the electrical equipment such as on the walls of residential units, offices and workshops.
This is the most common type of “high-voltage electrical box,” primarily composed of miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) and residual current devices (RCDs/RCBOs).
· Lighting Distribution Box: A distribution box specifically for powering and controlling lighting circuits. It typically only controls lighting circuits and does not include high-power socket circuits.
· Power Distribution Box/Cabinet: Specifically for powering and controlling motors, fans, pumps and other power equipment. It typically uses contactors, thermal relays and other control components that require higher capacity and circuit breaker breaking capacity.
· Control Box/Cabinet: Focuses on automatic or manual control of specific equipment or production processes, not just power distribution. It contains PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), relays, frequency converters, touch screens and other automation components.
· Metering Box: Primarily used to install electricity meters to measure electricity consumption in specific areas or for individual users. Its function is relatively simple.
By Structure and Enclosure
Installation Method
· Surface-Mounted Distribution Box: Directly installed on walls, columns or other surfaces. Easy to install, but takes up space and affects aesthetics.
· Concealed Distribution Boxes: Holes are pre-drilled in the wall to embed the box. Aesthetically pleasing and space-saving, they are the mainstream choice for new residential and office buildings.
Enclosure Material
· Metal Distribution Boxes: Such as cold-rolled steel plate, stainless steel, etc. High strength, good protection, and excellent heat dissipation; mainly used in industrial environments, outdoor applications or power distribution.
· Plastic Distribution Boxes: Such as engineering plastics (ABS, PC). It features good insulation, aesthetically pleasing and rust-resistant, but strength and heat resistance are not as good as metal. Mainly used in dry indoor environments such as residences and offices.
By Protection Rating
It comprises two digits that means dustproof and waterproof capabilities. For example, IP65.
· First digit (dustproof): 6 indicates the highest level of “dusttight” that completely prevent dust from entering.Second digit (waterproof): 5 indicates “spray-resistant” that prevent water spray from all directions.Select different protection ratings for the enclosure based on the installation environment.
· Standard type: such as IP30, IP40, prevents the ingress of solid foreign objects that is suitable for dry indoor environments.
· Splash-proof/Drip-proof type: such as IP54, IP55, prevents water spray from all directions and is suitable for humid, dusty workshops, kitchens, bathrooms, etc.
· Waterproof type: such as IP65, IP66, prevents strong water spray or brief immersion and is suitable for outdoor or very harsh industrial environments.
Other Special Types
· Explosion-proof distribution box: has a robust explosion-proof enclosure that isolates internal electric arcs or sparks from the external hazardous environment to prevent explosions. It is usually used in hazardous locations with flammable and explosive gases and dust (such as petroleum, chemical and coal mines).
· Outdoor distribution box: specifically designed for outdoor environments; the enclosure has good waterproof, dustproof, corrosion-resistant and UV-resistant capabilities with a protection rating typically above IP54.
· Intelligent distribution box: integrates power monitoring, data acquisition and communication functions (such as 4G/5G, Wi-Fi, and Ethernet). They can remotely monitor parameters such as voltage, current, power and energy in real time and provide fault alarms and intelligent control. They are an important component of smart grids and smart buildings.
Main Functions of DB Box
· Power Distribution: Safely and orderly distributes power from the autonomous power source to various independent branch circuits that supply power to electrical equipment in different areas.
· Overload Protection: Automatically cuts off power when the circuit current abnormally exceeds a safe value using circuit breakers or fuses to prevent overheating and fire risks.
· Electrical Equipment Protection: Prevents damage to connected electrical equipment due to short circuits, overloads and other faults to ensure equipment safety and lifespan.
· System Management and Monitoring: Centralized management of electrical components makes wiring clear that facilitate daily maintenance to improve management efficiency.
Applications of DB Box
Residential/Apartment Buildings
Typically each household has one distribution box that manages all electricity usage: the main switch, lighting circuits, general socket circuits (must have leakage protection), dedicated kitchen/bathroom circuits (must have leakage protection), air conditioning circuits, etc. Modern smart home distribution boxes also support remote control and power monitoring.
Commercial Buildings
In offices, shopping malls and hotels, in addition to regular lighting and socket distribution boxes, there are emergency lighting distribution boxes (powered by backup power in emergencies such as fires) and power distribution boxes (powering equipment such as water pumps and fans). High reliability and multiple circuits are required.
Factory/Workshop Buildings

Distribution boxes may contain industrial automation equipment such as frequency converters and PLC controllers, forming a power control center to power production lines, machine tools, robots and lighting systems.
High protection levels are required: typically IP54 and above, dustproof, waterproof, oil-proof and corrosion-resistant. It is provided with large capacity and uses robust materials with metal enclosures that are impact resistant.
Public Facilities and Outdoor Applications
Distribution boxes may be equipped with time-controlled or light-controlled switches for automatic control. Commonly used in road lighting control, traffic lights, communication base stations, park and squares. Extremely high protection rating: typically IP65 or higher with completely dustproof and rainproof.
Strong weather resistance: the enclosure and internal components can withstand ultraviolet radiation and extreme temperature changes.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
· Regular inspection: The electrical components of the distribution box need to be inspected regularly for aging wires, loose connections and damaged components to ensure safe system operation.
· Replace damaged components: Circuit breakers, fuses, etc., need to be replaced promptly when damaged to avoid affecting the normal operation of the power system.
Common faults include circuit breaker tripping, overheating of wires inside the distribution box, and leakage. When encountering these problems, first check whether the electrical connections are secure and whether the circuit is overloaded and then make appropriate repairs.
When a system requires the addition of new equipment or circuits, the distribution box can be upgraded or expanded to meet new power demands.
Summary
Distribution boxes are core devices for power distribution and protection that are widely used in homes, businesses and industries. Understanding their components, functions and maintenance methods ensures the safe and stable operation of the power system. Regular inspections and timely troubleshooting are crucial for ensuring the proper functioning of distribution boxes and selecting the appropriate distribution box type is also an important aspect of power system design.
QJC Electric offers a range of waterproof distribution boxes: HA-waterproof and HT-waterproof boxes. These are particularly suitable for special waterproof, dustproof and corrosion-resistant environments. For more information on power distribution box products, please click this link.